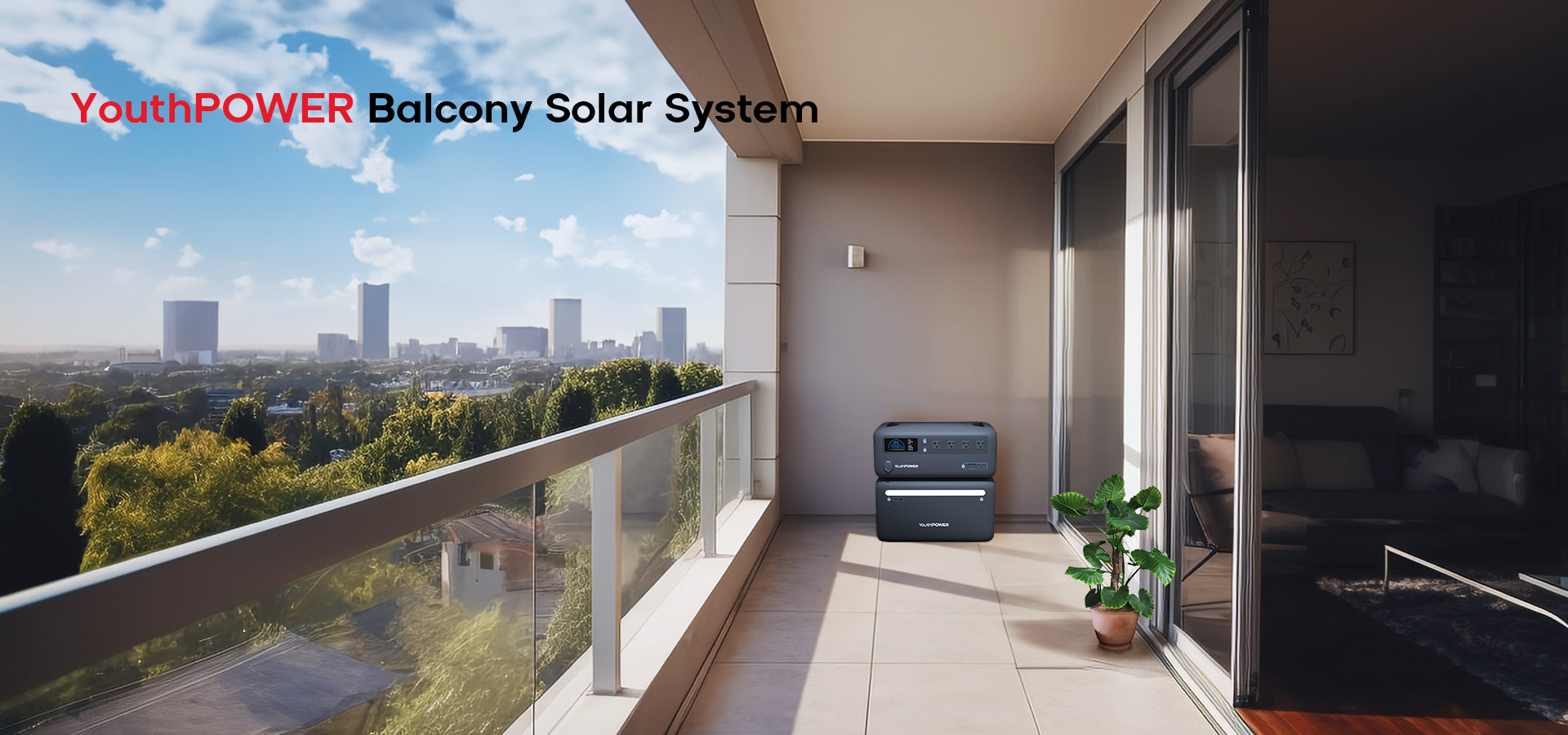
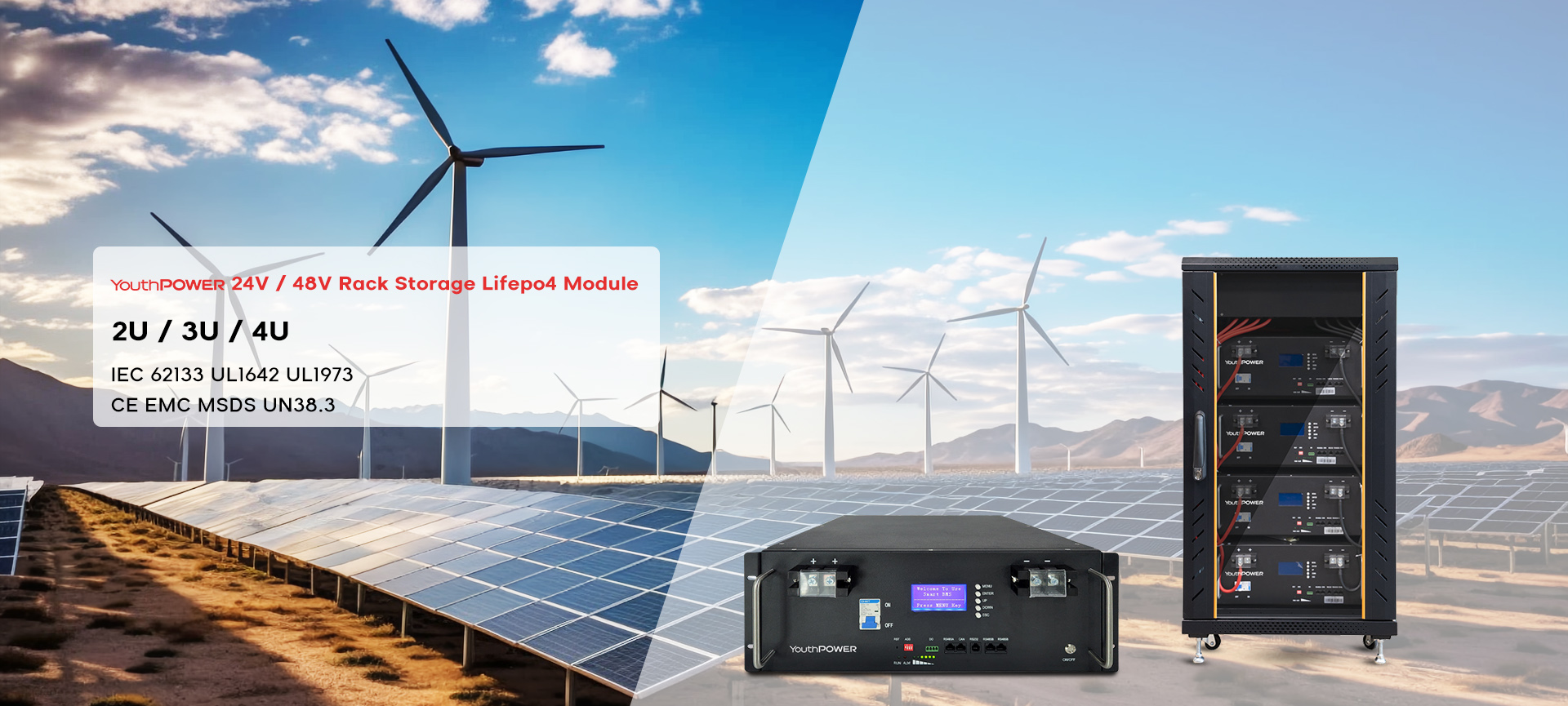
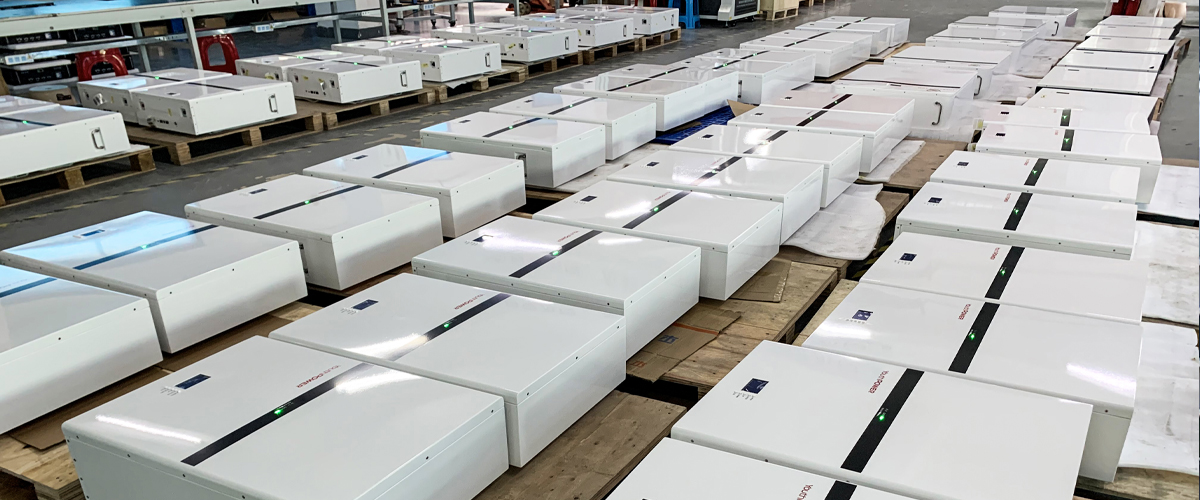
We Are Offering
About us
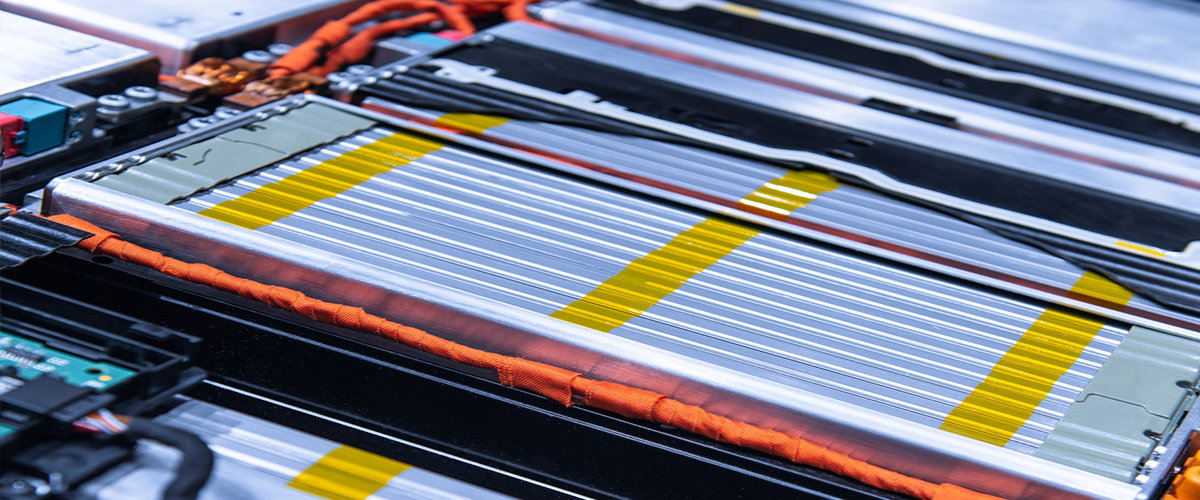
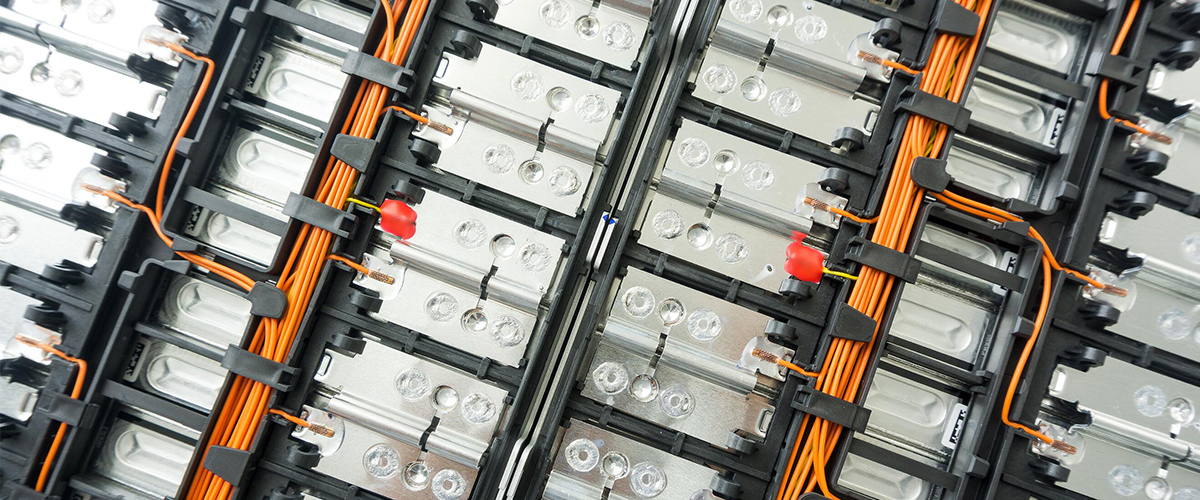
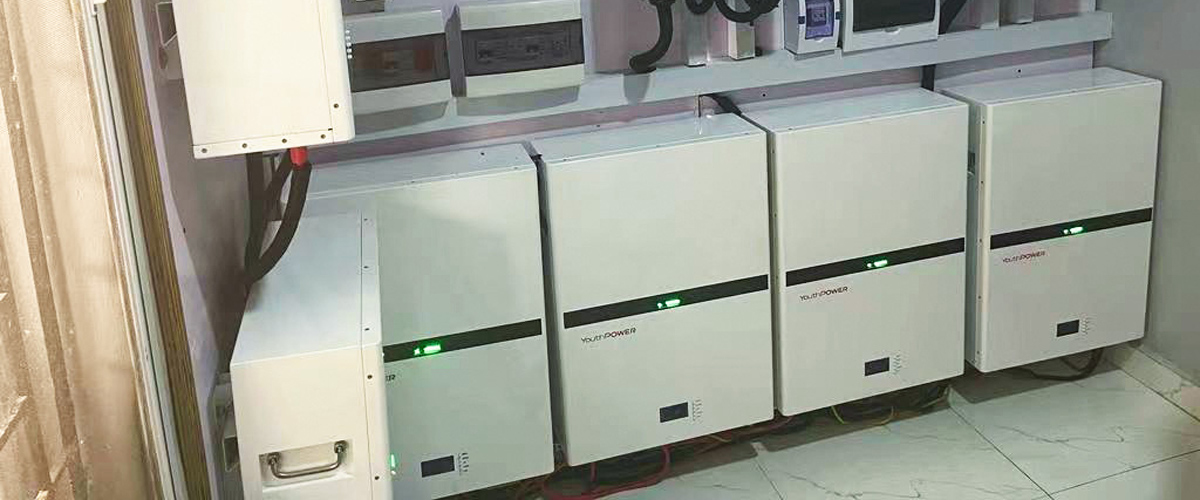
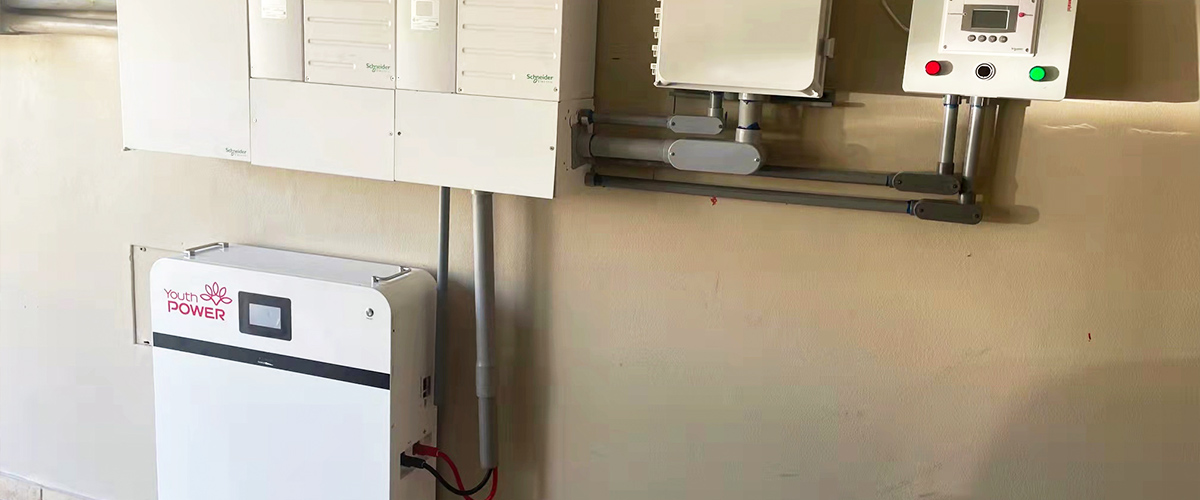
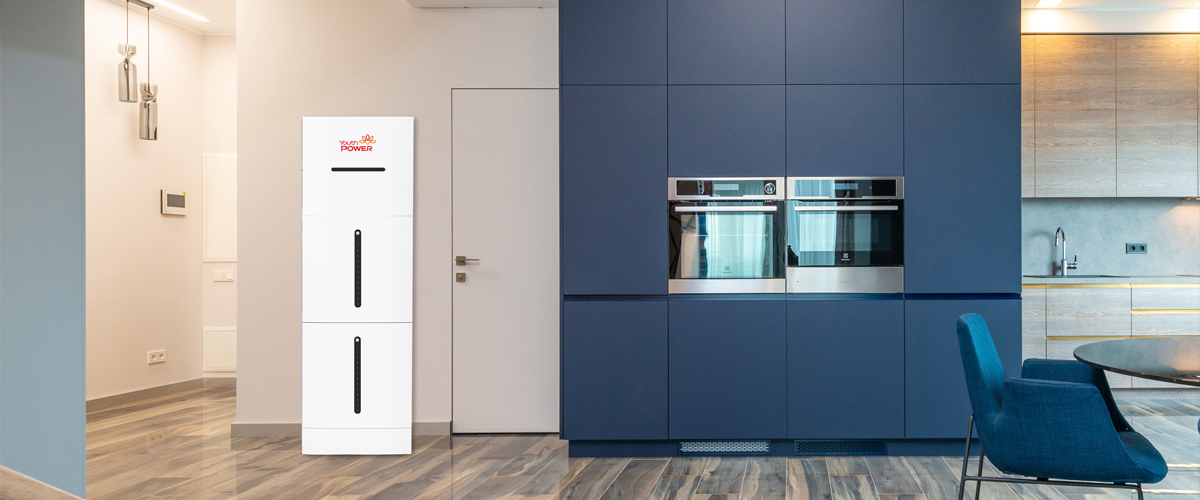
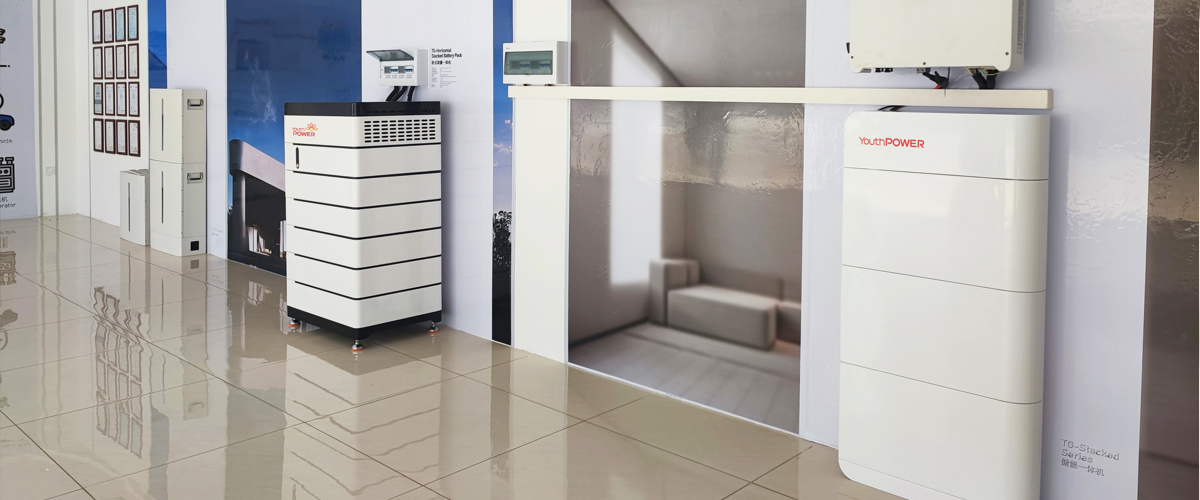
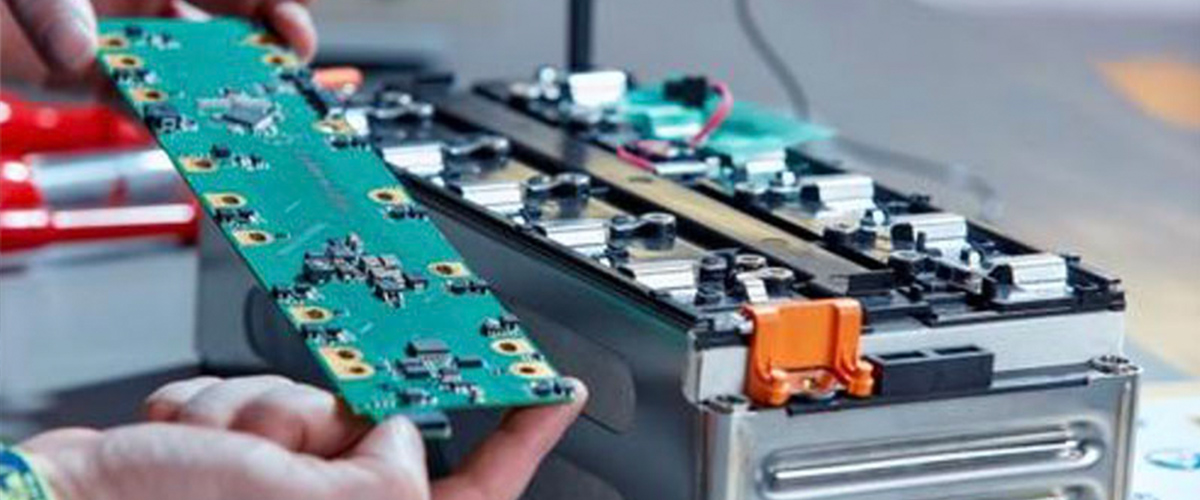
Founded in 2003, YouthPOWER has now become one of the leading suppliers of solar storage lithium batteries in the world. With a broad range of energy storage solutions, it covers a series of 12V, 24V, 48V and higher voltage lithium batteries solutions.
YouthPOWER has engaged in the battery technology and production for almost 20 years, with abundant manufacturing experience and strong new product R & D capability. Through many years of hard work and market promotion, we have created our own brand “ YouthPOWER ” in 2019. With nearly 20 years’ experience in the battery industry, we have the capability to provide you with both the products you need and the most suitable products you want. We are always ready to supply the first-class products and meet the various needs of the customers.